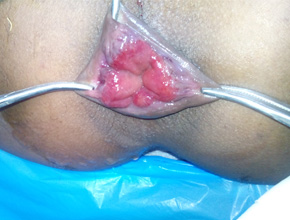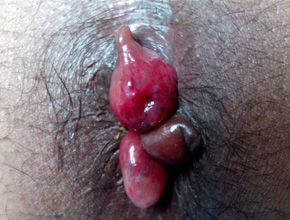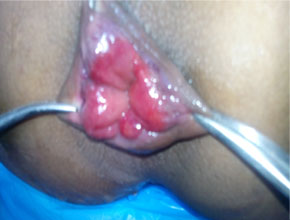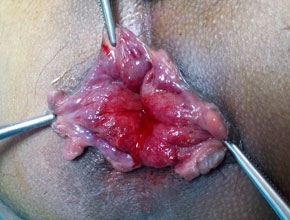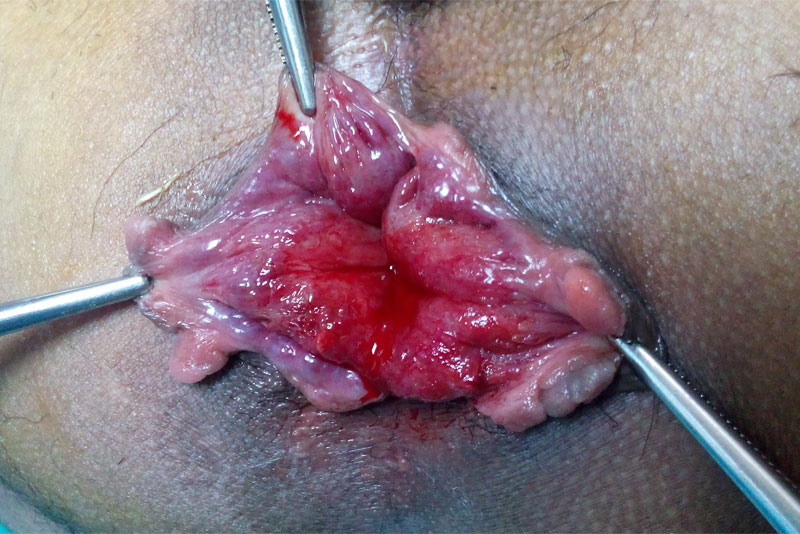
About Piles or Hemorrhoids
Piles is derived from Latin word ‘pilla’ means a ball. Hemorrhoids is a Greek word, Heama=Blood & Rhoids= flowing
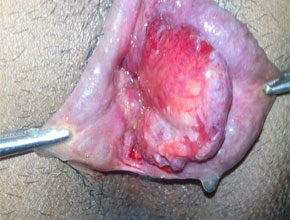
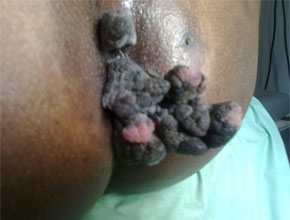
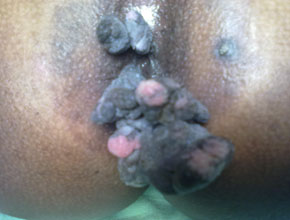
The varicosities of the veins in the anal-canal is called hemorrhoids.
It has divided mainly in external hemorrhoids & internal hemorrhoids.
Types: Internal & External
Position Wise: 11 O'Clock, 3 O'Clock, 7O'Clock
Gradation wise: Grade I, Grade II, Grade III, Grade IV
Clinical Features
- Complaints of bleeding P/R
- Pain during defection
- Discharge
- Anal irritation
- Prolapsed
- Secondary anemia
- Itching at perianal region
Treatment
- Conservative Management
- Fiber foods, laxatives, haemostatic, analgesics, anti hemorrhoids creams are used.
- Non – surgical Management
- Sclerotherapy, Rubberband, IRC, RF ablation.
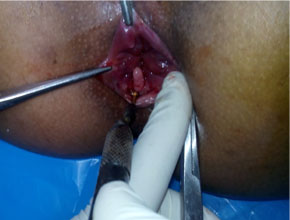
- Surgical management for grade IV hemorrhoids.
Do or Not To Do – For Piles Patients
Do :
- Do daily exercise like walking.
- Drink 8-10 glasses of water daily.
- Take fibers food. Maintain regular bowel habits.
Not To Do :
- Long standing/long sitting position
- Avoid spicy, chilly foods, Alcohol, excessive tea, coffee. It irritates the pile mass.
- Avoid constipation.
What causes Hemorrhoids?
The factors, which may be responsible in increasing abdominal pressure resulting into formation of haemorrhoids, include:
- Constant straining due to constipation.
- Diet high in processed food and low in fiber (noodles, cold drinks, fried food, etc.)
- Laxative abuse and frequent enemas.
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Obesity
- Lifting heavy objects
- Repeated coughing and sneezing
- Heredity : Frequently seen in the members of the same family presumably due to weakness of vein walls since birth.
- Pregnancy : Pressure of the fetus in the abdomen cause the blood vessels around the anus to enlarge.
- Some diseases/ conditions such as enlarged prostrate, urethral stricture (narrowing of the urinary opening) and cancer of rectum.
- Occupations involving :
- Lot of traveling (e.g. marketing and sales professionals)
- Prolonged standing (e.g. traffic police, waiters, etc.)
Symptoms of Hemorrhoids
Manifestations of hemorrhoids may vary depending upon the type of hemorrhoids.
External Hemorrhoids
- They may be quite painful as they lie under the skin that has rich supply of nerves.
- May appear as a tender blue swelling at the anal margin (due to thrombosis). Since the blood clot usually lies at the level of external sphincter muscles, anal spasm often occurs.
- Bleeding and itching in and around anus may also occur in some cases (due to co-existence of internal hemorrhoids, passage of hard stools or poor anal hygiene).
Internal Hemorrhoids
- Bleeding while passing the stool may be the only symptom in early stages. The bleeding is bright red in color and occurs as a “splash in the pan”.
- Prolapse of hemorrhoids is usually a later symptom. The degree of protrusion depends upon the progress of the disease.
- Feeling of vague anal discomfort usually accompanies bleeding. It increases when Piles protrudes through the anal opening.
- A mucoid (slimy) anal discharge and fecal leakage usually accompanies prolapsed haemorrhoids.
- Itching in and around the anal area follows mucoid discharge from the prolapsed hemorrhoids.
- Pain is not a common feature unless complicated by thrombosis (formation of blood clot), infection or erosion of the inner lining of the anal canal (mucosa).
Prevention of Hemorrhoids
The acute hemorrhoidal attacks can be prevented by preventing constipation. The safe and effective way to avoid constipation is increasing the fiber intake, regular morning walk and taking plenty of fluids.
Specific measures to prevent constipation include:
- Adding more fibers such as green leafy vegetables (palak, methi, broccoli), barley, rice bran, dalia, salads, fruits to the diet with minimal intake of tea, coffee and spices.
- Substituting refined flour (maida) by whole-wheat flour in home made preparations.
- Drinking at least 2 glasses of water/ lukewarm water or tea early in the morning will help in easy and comfortable evacuation.
- Increasing fluid intake especially in hot-humid weather (at least 10-12 glasses of water)
- Regular morning walk (brisk walking for at least 20 minutes every day.
Other measures include:
- Obese or overweight patient should be encouraged to lose weight.
- Natural urge for bowel movement should not be ignored.
- Lifting heavy weights should be avoided to the extent possible.
- Excessive straining during evacuation and prolonged sitting in the toilet should be avoided.